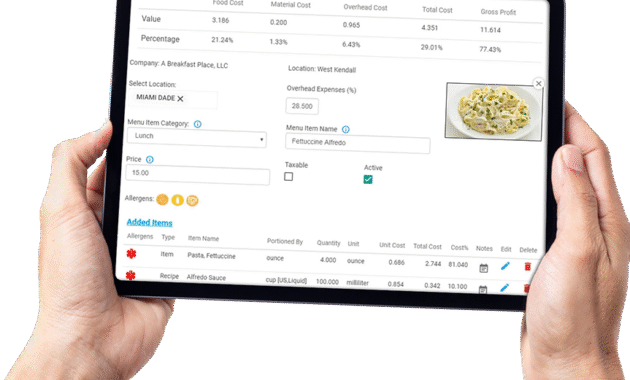
Delivery Apps That Specialize in Bulk Warehouse Orders have transformed the way businesses manage their supply chains, providing an efficient and streamlined approach to procurement. These applications cater to the unique needs of warehouses by enabling bulk ordering processes that save time and reduce costs. As the demand for quick and reliable logistics solutions grows, understanding how these apps function and the value they bring to the industry is essential for companies looking to optimize their operations.
The rise of e-commerce and global trade has highlighted the critical role of delivery apps in facilitating bulk transactions. By integrating advanced technologies and user-friendly interfaces, these platforms not only simplify the ordering process but also enhance inventory management and vendor selection. As businesses increasingly rely on bulk purchases, the importance of specialized apps that cater specifically to warehouse operations cannot be overstated.
In recent years, the topic of climate change and its effects on global ecosystems has garnered significant attention from researchers, policymakers, and the general public alike. The scientific consensus is clear: climate change, driven predominantly by human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes, is leading to a range of environmental changes that threaten the stability of ecosystems and human societies.
This article aims to explore the multifaceted impacts of climate change on biodiversity, ecosystems, and human health, while also examining potential mitigation strategies.Climate change refers to long-term alterations in temperature, precipitation patterns, and other atmospheric conditions. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reports indicate that global surface temperatures have risen by approximately 1.2 degrees Celsius since the late 19th century, primarily due to increased greenhouse gas emissions.
This warming is associated with a myriad of environmental changes, including rising sea levels, shifting weather patterns, and increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, droughts, and heatwaves.One of the most pressing concerns regarding climate change is its impact on biodiversity. Ecosystems around the world are experiencing shifts in species distributions, leading to mismatches between species and their habitats.
For instance, many plant species are blooming earlier in the spring due to mild winters, which can disrupt the life cycles of pollinators that rely on them. Additionally, rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns can create unsuitable habitats for many species, resulting in increased extinction rates. A study published in the journal “Nature” found that approximately one in six species may face extinction if global temperatures rise by more than 2 degrees Celsius.Marine ecosystems are particularly vulnerable to climate change.
Ocean warming and acidification, primarily due to increased carbon dioxide absorption, have devastating effects on coral reefs, which are among the most diverse ecosystems on the planet. Coral bleaching events, where corals lose their symbiotic algae due to stress from elevated temperatures, have become more frequent and severe. This not only threatens the coral themselves but also the myriad of species that depend on coral reefs for habitat and food.Furthermore, climate change exacerbates existing environmental stressors, such as habitat destruction and pollution, particularly for species already at risk.
For example, the polar bear, a species emblematic of climate change, faces habitat loss due to melting sea ice in the Arctic. As their hunting grounds diminish, polar bears are forced to travel greater distances in search of food, leading to increased mortality rates and declining populations.The implications of climate change extend beyond the natural world; they pose significant risks to human health and well-being.

Rising temperatures can lead to increased incidences of heat-related illnesses and mortality, particularly among vulnerable populations such as the elderly and those with pre-existing health conditions. Additionally, changes in climate can influence the spread of infectious diseases. For instance, warmer temperatures can expand the habitat range of disease-carrying mosquitoes, potentially increasing the incidence of diseases such as malaria and dengue fever in regions previously unaffected.Air quality is also impacted by climate change, as rising temperatures can exacerbate the formation of ground-level ozone, a harmful air pollutant.
Poor air quality is linked to respiratory diseases, cardiovascular problems, and premature mortality. Furthermore, extreme weather events can lead to disruptions in water supply, food production, and infrastructure, contributing to food insecurity and economic instability.Addressing the myriad challenges posed by climate change requires a multifaceted approach. Mitigation strategies must focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions across all sectors, including energy, transportation, and agriculture.
Transitioning to renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, is critical for decreasing reliance on fossil fuels. Additionally, enhancing energy efficiency in buildings and transportation systems can contribute to significant emissions reductions.Another essential aspect of climate change mitigation is the protection and restoration of natural ecosystems. Forests, wetlands, and mangroves serve as vital carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere.
Conserving these ecosystems not only helps mitigate climate change but also supports biodiversity and enhances resilience to climate impacts. Initiatives such as reforestation and afforestation can play a crucial role in this regard.Adaptation strategies are equally important in addressing the impacts of climate change that are already occurring. Building resilient infrastructure that can withstand extreme weather events, improving water management systems, and developing crop varieties that can thrive in changing conditions are all essential components of an effective adaptation strategy.
Additionally, investing in public health infrastructure and disease surveillance systems can help communities better prepare for and respond to climate-related health challenges.International cooperation and commitment are paramount in the global effort to combat climate change. The Paris Agreement, adopted in 2015, represents a significant milestone in climate diplomacy, with countries agreeing to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
However, the success of this agreement hinges on the willingness of nations to set and meet ambitious emissions reduction targets, as well as the provision of financial and technological support for developing countries that may struggle to implement necessary changes.In conclusion, climate change presents one of the most significant challenges of our time, with far-reaching consequences for biodiversity, ecosystems, and human health.
The urgency for action is clear, and it requires a concerted effort across all sectors of society. By prioritizing both mitigation and adaptation strategies, we can work towards a sustainable future that protects our planet and its inhabitants. Collaborative efforts, innovative solutions, and a commitment to sustainable practices will be essential in addressing the complex and interrelated challenges posed by climate change.
The time to act is now, as the stakes for our planet’s future and the well-being of generations to come are immeasurable.